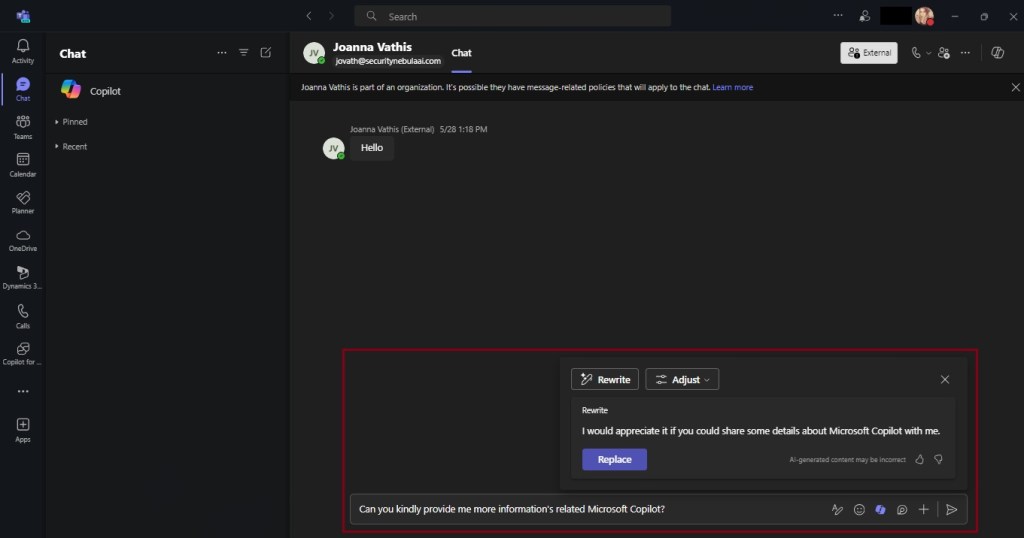
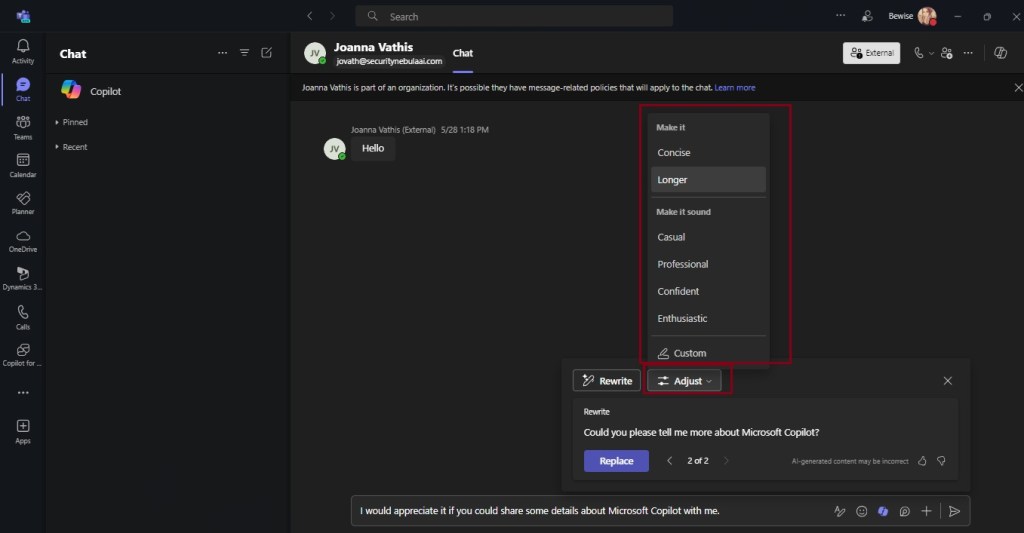
Microsoft 365 Copilot is a sophisticated processing and orchestration engine that provides AI-powered productivity capabilities by coordinating the following components:
- Large language models (LLMs)
- Content in Microsoft Graph, such as emails, chats, and documents that you have permission to access.
- The Microsoft 365 productivity apps that you use every day, such as Word and PowerPoint.
How does Microsoft 365 Copilot use your proprietary organizational data?
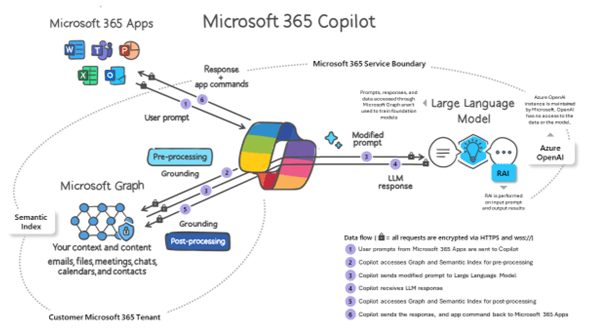
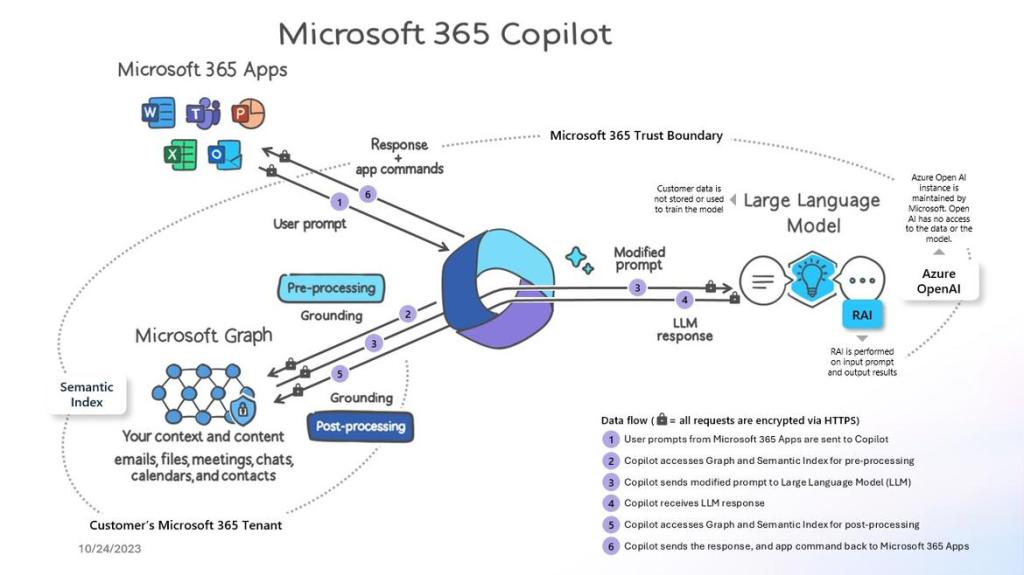
Microsoft 365 Copilot provides value by connecting LLMs to your organizational data. Microsoft 365 Copilot accesses content and context through Microsoft Graph. It can generate responses anchored in your organizational data, such as user documents, emails, calendar, chats, meetings, and contacts. Microsoft 365 Copilot combines this content with the user’s working context, such as the meeting a user is in now, the email exchanges the user had on a topic, or the chat conversations the user had last week. Microsoft 365 Copilot uses this combination of content and context to help provide accurate, relevant, and contextual responses.
Microsoft 365 Copilot only surfaces organizational data to which individual users have at least view permissions. It’s important that you’re using the permission models available in Microsoft 365 services, such as SharePoint, to help ensure the right users or groups have the right access to the right content within your organization. This includes permissions you give to users outside your organization through inter-tenant collaboration solutions, such as shared channels in Microsoft Teams.
When you enter prompts using Microsoft 365 Copilot, the information contained within your prompts, the data they retrieve, and the generated responses remain within the Microsoft 365 service boundary, in keeping with our current privacy, security, and compliance commitments. Microsoft 365 Copilot uses Azure OpenAI services for processing, not OpenAI’s publicly available services. Azure OpenAI doesn’t cache customer content and Copilot modified prompts for Microsoft 365 Copilot.
Data stored about user interactions with Microsoft 365 Copilot
When a user interacts with Microsoft 365 Copilot (using apps such as Word, PowerPoint, Excel, OneNote, Loop, or Whiteboard), we store data about these interactions. The stored data includes the user’s prompt and Copilot’s response, including citations to any information used to ground Copilot’s response. We refer to the user’s prompt and Copilot’s response to that prompt as the “content of interactions” and the record of those interactions is the user’s Copilot activity history. For example, this stored data provides users with Copilot activity history in Microsoft 365 Copilot Chat (previously named Business Chat) and meetings in Microsoft Teams. This data is processed and stored in alignment with contractual commitments with your organization’s other content in Microsoft 365. The data is encrypted while it’s stored and isn’t used to train foundation LLMs, including those used by Microsoft 365 Copilot.
To view and manage this stored data, admins can use Content search or Microsoft Purview. Admins can also use Microsoft Purview to set retention policies for the data related to chat interactions with Copilot. For Microsoft Teams chats with Copilot, admins can also use Microsoft Teams Export APIs to view the stored data.

Deleting the history of user interactions with Microsoft 365 Copilot
Your users can delete their Copilot activity history, which includes their prompts and the responses Copilot returns, by going to the My Account portal. More information, see Delete your Microsoft 365 Copilot activity history.

Microsoft 365 Copilot and the EU Data Boundary
Microsoft 365 Copilot calls to the LLM are routed to the closest data centers in the region, but also can call into other regions where capacity is available during high utilization periods.
For European Union (EU) users, we have additional safeguards to comply with the EU Data Boundary. EU traffic stays within the EU Data Boundary while worldwide traffic can be sent to the EU and other countries or regions for LLM processing. The EU Data Boundary is a geographically defined boundary within which Microsoft has committed to store and process Customer Data and personal data for our Microsoft enterprise online services, including Azure, Dynamics 365, Power Platform, and Microsoft 365, subject to limited circumstances where Customer Data and personal data will continue to be transferred outside the EU Data Boundary.
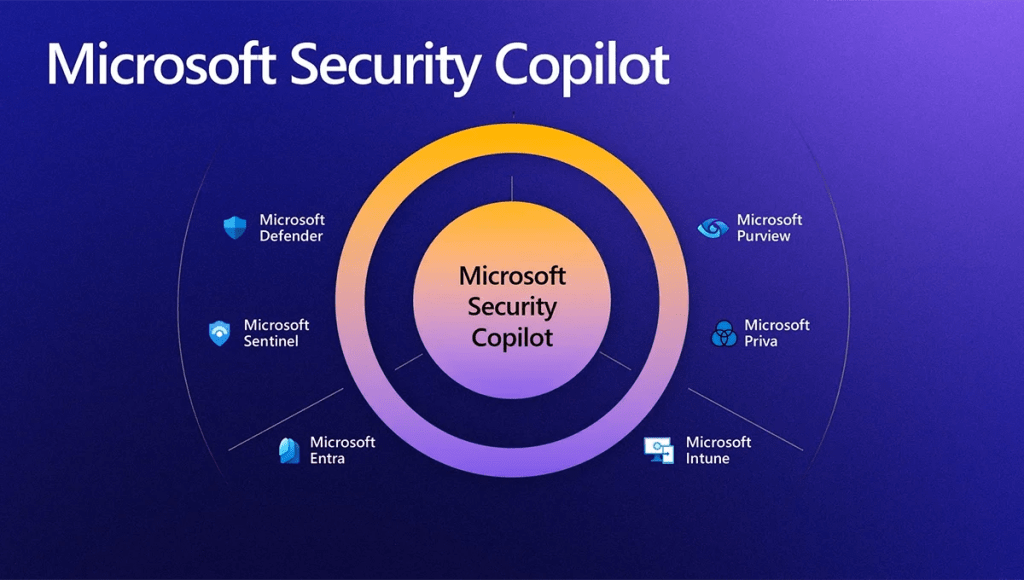
How does Microsoft 365 Copilot protect organizational data?
The permissions model within your Microsoft 365 tenant can help ensure that data won’t unintentionally leak between users, groups, and tenants. Microsoft 365 Copilot presents only data that each individual can access using the same underlying controls for data access used in other Microsoft 365 services. Semantic Index honors the user identity-based access boundary so that the grounding process only accesses content that the current user is authorized to access.
Copilot works together with your Microsoft Purview sensitivity labels and encryption to provide an extra layer of protection. The following diagram provides a visual representation of how Copilot honors your information protection controls using sensitivity labels and encryption.

Copilot will only work with your M365 tenant data and won’t be able to access other companies’ data. Plus, your data doesn’t train the AI for other companies to leverage..